Food delivery has become a new normal after the arrival of the global COVID-19 pandemic, with many strong statistics to back it up. According to Statista, the number of users in the on-demand food delivery industry is anticipated to touch a whopping 2.5 billion by 2027.
After all, food delivery apps offer unmatched convenience, allowing people to order their favorite meals with a few taps on their smartphones. This eliminates the need for cooking, dining out or waiting in long queues.
As the food delivery marketplace app, Postmates continues to achieve remarkable success, it has piqued the interest of a growing number of investors looking to fund similar applications.
Thus, it’s the perfect time for aspiring entrepreneurs to tap into this thriving market by launching an app like Postmates.
What is Postmates?
Postmates is an on-demand food delivery marketplace that operates in up to 100 metropolitan regions in the United States. It allows users to order food, groceries and other goods from local businesses and deliver them to their doorstep. It is one of the oldest and most popular food delivery apps in the United States and is now a part of the Uber family.

Postmates Business Model: Decoding Its Business Strategy
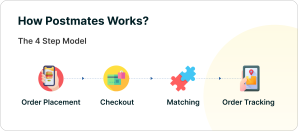
Postmates works on the platform-to-consumer business model, connecting customers with nearby restaurants and stores. Customers can place orders for food, groceries and various items, and these orders are fulfilled by independent delivery partners who bring the requested items right to the customers’ doorsteps.
Here is a step-by-step overview of how Postmates works:
Step 1: Order Placement
Customers use the Postmates app or website to explore various local restaurants, grocery stores, and retailers. Whether it’s a favorite meal from a nearby restaurant, groceries for the week or essential retail products, Postmates offers a convenient platform for customers to select the items they want and add them to their virtual shopping cart.
Step 2: Checkout
After completing their selection, customers proceed to the payment and address section of the app. Here, they provide essential information, including their delivery address and payment method. Postmates ensures security and convenience by allowing various payment options, such as /debit card, cash on delivery, PayPal, etc.
Step 3: Matching
Once the order details are confirmed, Postmates’ intelligent system works behind the scenes. It automatically assigns a nearby courier or delivery driver to the order. These couriers are often independent contractors who utilize their own modes of transportation, whether it’s a car, bike, or even walking, to pick up and deliver the requested items.
Step 4: Order Tracking
With the order now assigned, the delivery driver embarks on the journey to fulfill the customer’s request. They first collect the order from the chosen restaurant, store, or merchant. Customers can track the progress of their delivery in real time through the app, which includes a map displaying the courier’s current location. After the successful delivery, customers can rate their courier and express their satisfaction through tips.
Postmates Revenue Model: A Deep Dive into Its Revenue Streams
When it comes to building a food delivery marketplace app like Postmates, you should deep delve into its revenue model. Postmates has a revenue model built around multiple streams that allow the company to generate decent money. Here are Postmates’ primary revenue streams:
1. Delivery Fees
One of the primary sources of revenue for Postmates is delivery fees. Customers are charged a fee for each delivery made through the platform. This fee could vary based on factors like distance, location and demand.
2. Service Fees
Postmates imposed service fees on orders. These fees cover the operational costs of maintaining the platform, providing customer support and other essential services. The service fee is a flat 9% of the total order amount.
3. Merchant Commissions
Postmates partners with a wide range of local restaurants, grocery stores and retailers. In exchange for bringing in customers and facilitating orders, Postmates earns commissions or fees from these merchant partners. These fees were typically calculated as a percentage of the total order value.
4. Postmates Unlimited Subscription
Postmates offers a subscription service called Postmates Unlimited. Subscribers pay a $9.99 monthly or $99.99 annual fee to enjoy benefits such as waived delivery fees on orders above a certain amount and access to exclusive perks. This subscription model aims to generate recurring revenue and encourage customer loyalty.
From Idea to Launch: A Step-by-Step Guide on How to Build an App Like Postmates?
It’s time to answer the main question: how to build an app like Postmates?
Building food delivery marketplaces like Postmates involves a series of steps, from ideation to marketing your app. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to make an app like Postmates:
Step 1: Research the market
Begin by conducting thorough market research to understand the on-demand delivery industry, customer needs and competition. This will help you determine your unique value proposition: what sets your app apart from existing competitors like Postmates. Your unique features or offerings will be a key selling point.
- Identify existing food delivery marketplace services in your target area. Study their business models, strengths, weaknesses and features.
- Analyze the pricing strategies of competitors and evaluate the profitability of different pricing models.
- Keep pace with changing customer demands and their purchasing behavior to come up with features that deliver a superior experience to them.
- Understand the regulatory environment for food delivery services in your region. Research permits, licenses, health and safety standards and any legal requirements.
- Study user reviews and feedback on existing platforms to identify pain points, areas of improvement and features that resonate with customers.
Step 2: Choose a business model and revenue strategy
The next step is to choose the business and revenue model for your on-demand food delivery marketplace business. How will you make money from your app? Will you charge customers delivery fees, service fees, or both? Will you also charge merchants a commission? Your revenue strategy will depend on the business model you choose.
There are three main types of food delivery business models:
- The Order Only Model: In this model, your platform primarily focuses on receiving customer orders and forwarding them to partnering merchants. The responsibility for meal preparation and delivery lies entirely with the merchants. Example: Grubhub.
- The Order and Delivery Model: This model involves both receiving customer orders and managing the delivery process. While partnering with merchants for food preparation, your business takes charge of the delivery logistics. You may employ a fleet of drivers or utilize third-party delivery services to ensure timely and efficient deliveries. Example: Uber Eats
- The Fully Integrated Model: The fully integrated model encompasses all aspects of the food delivery process, from receiving orders and preparing food to managing deliveries. In this model, you might operate cloud kitchens or virtual restaurants to prepare meals, ensuring consistency and quality. Example: McDonald’s.
Step 3: Choose key features of your food delivery marketplace
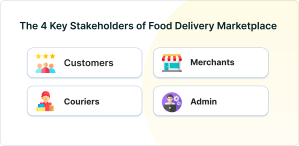
In the food delivery marketplace business, four key stakeholders play essential roles in the ecosystem. These stakeholders contribute to the success and operation of the marketplace. To cater to the unique needs of each stakeholder, dedicated apps must be developed. Let’s explore these key stakeholders and delve into the distinct features tailored to their requirements:
-
Customers
They are at the core of the food delivery marketplace. They place orders, pay for deliveries, and provide feedback. Their satisfaction is critical for the success of the platform.
- Key Features: Ordering food online, browsing menus, tracking deliveries, providing reviews and ratings and accessing promotions and discounts.
-
Restaurants or Merchants
Restaurants partner with food delivery marketplaces to list their menus and offer delivery services. They prepare and package the food, which is then delivered to customers by drivers or couriers.
- Key Features: Listing menus on the platform, receiving and processing orders, managing inventory, receiving payments, accessing customer data and analytics.
-
Delivery Drivers or Couriers
Independent delivery drivers or couriers are responsible for picking up orders from restaurants and delivering them to customers. They play a crucial role in ensuring timely and efficient delivery.
- Key Features: Accepting delivery requests, picking up and delivering orders, using navigation tools, communicating with customers, and tracking earnings.
-
Marketplace Admin
It is the operator of the food delivery marketplace that manages the platform and handles customer support, marketing, technology development, and partnerships with restaurants and drivers.
- Key Features: Customer management, order management, menu management, restaurant management, delivery staff management, payment & commission tracking, customer support
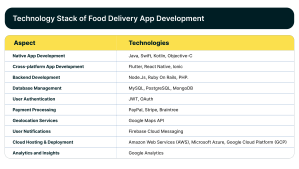
Step 4: Pick the right technology stack
The technology stack refers to the combination of programming languages, frameworks, libraries, databases and tools used to build a marketplace app. When it comes to how to build an app like Postmates, choosing the right tech stack is pivotal as it serves as the foundation for delivering a smooth user experience.
Whether you decide to build your food delivery app only for Android or iOS or both platforms, you might need different technologies to realize your idea.
For example, building an app for Android and iOS through a native app development approach requires creating separate codebases, as the two platforms have different programming languages (Swift for iOS, Java/Kotlin for Android).
On the other hand, if you go for a cross-platform development approach to build your food delivery for both Android and iOS using a single codebase, you need to include React Native or Flutter in your tech stack.
Step 5: Hire an on-demand marketplace app development company
Building a food delivery marketplace app like Postmates requires a range of tech resources to ensure successful development, launch and ongoing operation such as a UI/UX designer, Android developer, iOS developer, business analyst and QA & testing engineer. A reliable on-demand marketplace development company is armed with a full-scale development team to extend support from development to deployment and ongoing maintenance.
Step 6: Build an MVP
You should work with an on-demand food delivery marketplace app development company with expertise in MVP app development for startups.
An MVP or Minimum Viable Product represents the app’s basic version, featuring core functionalities that convey the app’s core purpose without including the full array of advanced features. The idea behind building an MVP is to gauge user interest and market demand with minimal investment. It helps verify if your app idea resonates with users before committing to full-scale development.
Step 7: Perform rigorous testing
While it may be tempting to skip thorough testing when working with a tight budget, quality assurance (QA) remains a pivotal component in launching a successful marketplace app. Given the fierce competition in on-demand food delivery marketplace app development, continuous QA and performance testing must be integrated throughout the entire project lifecycle. This proactive approach enables you to pinpoint and rectify any bugs, ensuring that the marketplace undergoes necessary improvements before its launch to customers.
Step 8: Rollout your food delivery marketplace
After testing your app, the next step is to submit it to either the Apple App Store or Google Play Store or both depending on the targeted platforms. However, it’s essential to adhere to the respective developer guidelines set forth by Google and Apple when submitting your marketplace app to these platforms.
Step 9: Post-launch maintenance
After successfully launching your marketplace on Play Store/App Store, the next and continuous step is the maintenance of your food delivery marketplace to ensure that it continues to function smoothly, remains up to date and keeps pace with evolving user expectations.
Step 10: Market your food delivery marketplace
In the fiercely competitive landscape of the food delivery industry with many strong key players already vying for market share, it is essential to get your marketplace noticed and downloaded by users. This means leveraging data-driven growth marketing strategies for food delivery apps such as social media marketing, hyper-targeting and email marketing to drive user acquisition, engagement, revenue and long-term success for your food delivery marketplace app.
How Can InfoStride Help in Launching Your Food Delivery Business?
InfoStride is renowned for its tailored on-demand food delivery marketplace app development solutions, covering the entire spectrum from initial idea conceptualization to design, development, deployment and growth marketing. Our seasoned team comprises skilled consultants and developers with an in-depth knowledge of the on-demand food delivery sector.
Whether you aspire to develop a food delivery app like Uber Eats, DoorDash or Postmates, our experts are well-equipped to steer you through the entire on-demand food delivery app development journey, elevating your business to new heights.
Reach out to us today and let’s get started.
FAQs
1. How much does it cost to build an app like Postmates?
The food delivery app development cost like Postmates can range from $40,000 to $300,000, depending on a number of factors, including the complexity of the app, the features you want to include, the development team you hire and the chosen technology stack. It’s best to consult with experts to get an accurate estimation to build your own food delivery app.
2. How long does it typically take to develop a food delivery app like Postmates?
Development time can vary but may range from several months to over a year, depending on the complexity of the app and the size of your development team.
3. Can I use third-party services for certain features, like payment processing and mapping?
Yes, using third-party services can reduce development time and costs. Many food delivery marketplace apps leverage services like Stripe for payments and Google Maps for mapping.
4. What ongoing costs should I anticipate after launching the app?
Ongoing costs include server hosting, payment gateway fees, marketing expenses, app updates, customer support and maintenance. You should budget for these to ensure smooth operations.