Digital accessibility refers to the practice of designing and developing digital platforms—such as websites, mobile apps, and other online tools—in a way that makes them usable by everyone, including people with disabilities. This encompasses a broad range of disabilities, including visual, auditory, physical, speech, cognitive, and neurological impairments. The goal of digital accessibility is to ensure that all users, regardless of their abilities, can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with the digital world.
Ensuring digital accessibility is not just about compliance with legal standards; it is a fundamental aspect of inclusivity and equity. By making digital platforms accessible, we can provide equal opportunities for all individuals to participate in the digital economy, access information, and communicate effectively. This is particularly important in an era where so many aspects of life—such as education, employment, healthcare, and social interaction—are increasingly conducted online.
Why Digital Accessibility Matters in 2024
In 2024, the importance of digital accessibility is more pronounced than ever. There is a growing emphasis on inclusivity and diversity, driven by societal shifts and a heightened awareness of the needs of underrepresented groups. Ensuring digital accessibility aligns with these values, fostering a more inclusive digital environment where everyone has the opportunity to succeed. For a more in-depth discussion on why is web accessibility important, refer to our detailed blog post on this topic.
Ongoing Challenges in Digital Accessibility
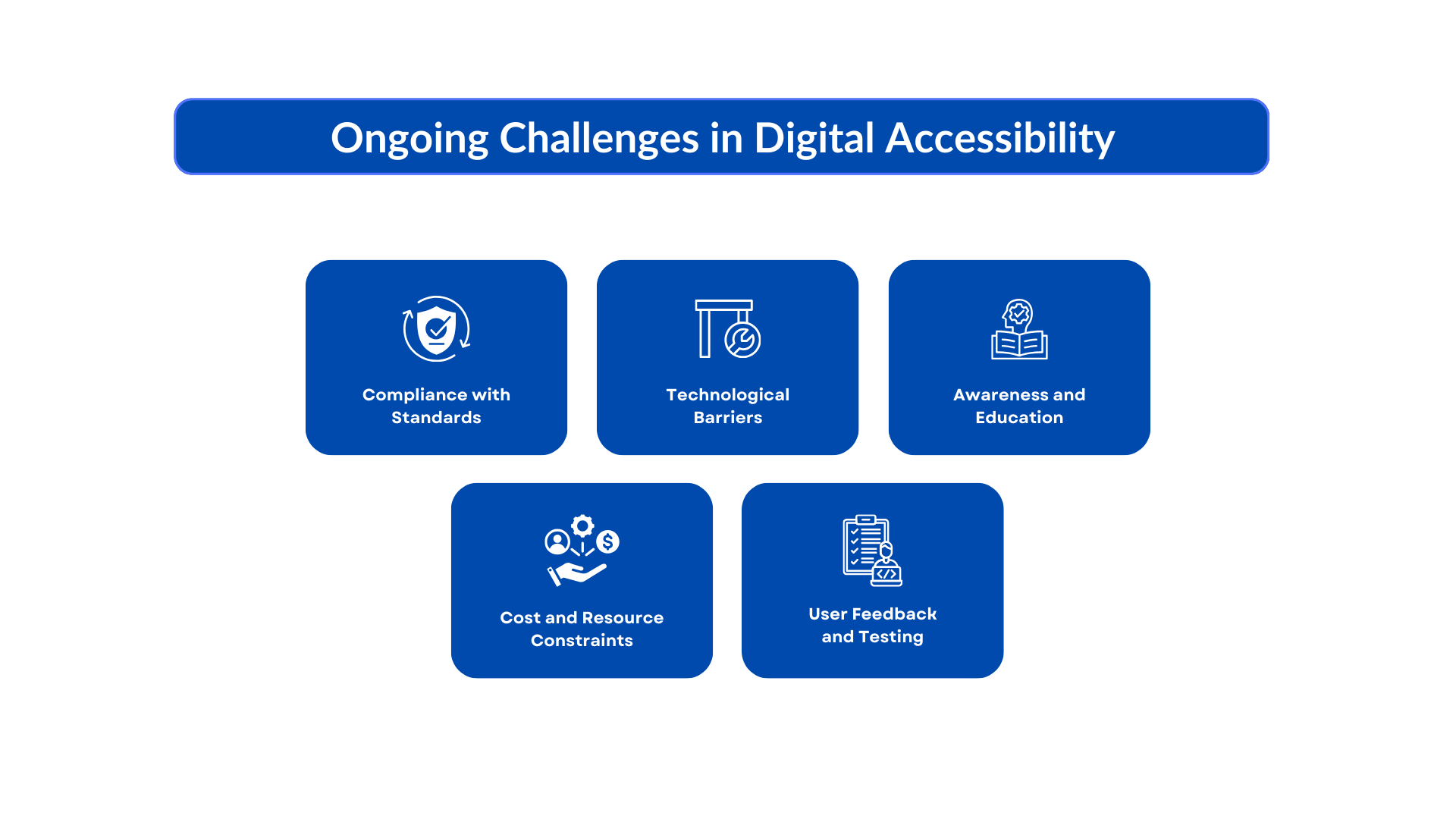
Achieving full digital accessibility continues to face several persistent challenges:
-
Compliance with Web Accessibility Standards:
Many organizations struggle to keep up with evolving web accessibility standards and regulations. Ensuring compliance requires continuous effort and investment in accessibility testing and updates, which can be resource-intensive.
-
Technological Barriers:
Certain technologies still pose significant barriers to accessibility. For example, complex interactive content, such as dynamic web applications and multimedia, can be difficult to make fully accessible. Additionally, while AI and machine learning offer new possibilities, they also present challenges in terms of accuracy and consistency.
-
Awareness and Education:
A lack of awareness and understanding of digital accessibility among designers, developers, and decision-makers remains a major hurdle. Many professionals are not fully equipped with the knowledge and skills needed to implement accessibility features effectively.
-
Cost and Resource Constraints:
Implementing and maintaining accessibility features can be costly, particularly for small businesses and organizations with limited resources. This financial barrier often leads to delayed or insufficient accessibility measures.
-
User Feedback and Testing:
Regular user feedback and comprehensive testing are crucial for maintaining accessibility, but they are often overlooked. Ensuring that digital platforms meet the needs of all users requires ongoing engagement with the disability community and iterative improvements based on their feedback.
In summary, while the previous year saw significant strides in digital accessibility, there are still substantial challenges to overcome. Addressing these issues will require concerted efforts from all stakeholders, including businesses, developers, policymakers, and users.
Emerging Trends in Digital Accessibility for 2024

AI and Machine Learning Enhancements
In 2024, AI and machine learning will continue to revolutionize digital accessibility by providing more intuitive and personalized user experiences. Key advancements include:
1. AI-Powered Captioning:
AI-driven captioning tools have become more accurate and reliable, offering real-time transcription for videos, webinars, and live streams. This enhancement significantly benefits users with hearing impairments, enabling them to access auditory content with ease.
2. Voice Recognition:
Voice recognition technologies have advanced, allowing for more precise and faster speech-to-text conversion. This improvement is crucial for users with mobility impairments or those who prefer voice input over traditional typing.
3. Personalized User Experiences:
Machine learning algorithms are now capable of learning individual user preferences and adapting interfaces accordingly. This personalization enhances accessibility by tailoring content presentation and navigation to suit specific needs, making digital interactions more user-friendly.
Voice User Interfaces (VUIs)
The rise of voice-controlled devices and applications has marked a significant shift in digital accessibility. VUIs provide several benefits for users with disabilities:
1. Hands-Free Interaction:
VUIs allow users to interact with devices without needing to use their hands, which is especially beneficial for individuals with mobility impairments.
2. Ease of Use:
Voice commands simplify complex tasks and navigation, reducing cognitive load and making it easier for users with various disabilities to operate digital devices.
3. Wide Adoption:
The widespread adoption of smart speakers, virtual assistants, and voice-enabled apps means that more people can benefit from these accessibility features in their daily lives.
Augmented and Virtual Reality (AR/VR)
AR and VR technologies hold great potential for creating accessible virtual environments, with several innovations making them more inclusive:
1. Accessible VR Environments:
Developers are designing VR experiences with accessibility in mind, incorporating features like adjustable text size, color contrast options, and alternative input methods to accommodate users with visual and motor impairments.
2. AR Assistance:
AR applications are being developed to provide real-time assistance to users with disabilities. For example, AR glasses can offer navigation help for visually impaired users by overlaying directions on their field of view.
Advanced Web and Mobile App Accessibility Features
2024 sees significant advancements in the accessibility of websites and mobile apps, focusing on innovative design and functionality:
1. Responsive Design Enhancements:
Improved responsive design techniques ensure that digital content is accessible on various devices, from desktops to smartphones, catering to diverse user needs.
2. Enhanced Screen Reader Compatibility:
Web and app developers are implementing better screen reader compatibility, providing more descriptive alt text for images and ensuring that interactive elements are easily navigable via keyboard and voice commands.
Focus on Cognitive Accessibility
Trends in 2024 highlight the importance of addressing cognitive accessibility, with new tools and design principles aimed at simplifying user experiences:
1. Simplified Interfaces:
Designers are creating more straightforward, clutter-free interfaces that reduce cognitive load and make it easier for users with cognitive disabilities to navigate digital platforms.
2. Guided Assistance:
Tools offering step-by-step guidance and prompts help users with cognitive impairments complete tasks independently and confidently.
Legislation and Policy Changes
Upcoming legal requirements and policy changes are shaping the future of digital accessibility:
1. Stricter Web Accessibility Standards:
Governments worldwide are implementing more rigorous web accessibility standards, requiring businesses to ensure their digital platforms are compliant. Failure to comply can result in legal consequences and damage to reputation.
2. Incentives for Accessibility:
Some regions are introducing incentives for organizations that prioritize accessibility, such as tax breaks or grants for developing accessible technologies.
3. Global Harmonization of Standards:
Efforts are being made to harmonize accessibility standards across different countries, making it easier for multinational companies to comply and ensuring a consistent level of accessibility worldwide.
How Businesses and Developers Need to Adapt
To stay ahead of these emerging trends and regulatory changes, businesses and developers must:
1. Invest in Accessibility Training:
Regular training sessions for design and development teams to keep them updated on the latest accessibility best practices and tools.
2. Incorporate Accessibility from the Start:
Embed accessibility considerations into the early stages of design and development processes to avoid costly retrofits and ensure a more inclusive user experience.
3. Leverage User Feedback:
Engage with users with disabilities to gather feedback and insights, using this information to inform continuous improvements and ensure platforms meet their needs effectively.
By embracing these trends and adapting to new requirements, businesses can create more inclusive digital experiences and demonstrate their commitment to accessibility in 2024 and beyond.
Technological Innovations Driving Accessibility
AI and Accessibility
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a pivotal role in revolutionizing digital accessibility, offering innovative solutions that enhance the usability of digital platforms for people with disabilities. Some notable AI applications and tools include:
1. AI-Powered Captioning and Subtitling:
Advanced AI algorithms are now capable of generating highly accurate real-time captions and subtitles for video content. Tools like Google’s Live Caption and Microsoft’s Azure Cognitive Services provide on-the-fly captioning for live streams, meetings, and pre-recorded videos, making content accessible to those with hearing impairments.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP):
NLP technologies are improving the accessibility of written content by offering tools for text simplification and language translation. For example, AI-based tools like Grammarly and QuillBot can simplify complex text, making it more comprehensible for users with cognitive disabilities.
3. Voice Assistants and Chatbots:
AI-driven voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, Google Assistant, and Apple’s Siri are becoming more sophisticated, providing hands-free interaction and personalized assistance to users. Additionally, AI-powered chatbots on websites and apps offer accessible customer support, helping users navigate services and find information without relying on traditional input methods.
4. Image Recognition and Description:
AI tools like Microsoft’s Seeing AI and Google’s Lookout use image recognition technology to provide audio descriptions of visual content. These applications help visually impaired users understand their surroundings and interact with visual media more effectively.
Assistive Technologies
Emerging assistive technologies are transforming how individuals with disabilities interact with digital platforms. Key innovations include:
1. Wearable Assistive Devices:
Wearable technologies, such as smart glasses and hearing aids integrated with AI, offer enhanced accessibility features. For example, OrCam MyEye is a wearable device that reads text aloud and recognizes faces, empowering visually impaired users to navigate their environments independently.
2. Adaptive Input Devices:
New adaptive input devices, such as eye-tracking systems and brain-computer interfaces, provide alternative ways for users with severe physical disabilities to control computers and mobile devices. Tobii Dynavox, for instance, offers eye-tracking technology that enables users to operate digital devices using only their eye movements.
3. Assistive Mobile Apps:
A variety of assistive mobile applications are being developed to support individuals with disabilities. Apps like Be My Eyes connect visually impaired users with sighted volunteers for real-time assistance, while apps like Proloquo2Go offer augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools for individuals with speech impairments.
Cross-Platform Accessibility Solutions
Ensuring accessibility across different platforms is crucial for creating a seamless user experience. Several tools and frameworks are driving cross-platform accessibility:
1. Universal Design Principles:
Universal design principles advocate for designing digital content that is inherently accessible to all users, regardless of the platform. By following these principles, developers can create interfaces that are functional and user-friendly across various devices, from desktops to mobile phones.
2. Responsive Design Frameworks:
Responsive design frameworks, such as Bootstrap and Foundation, allow developers to build websites that automatically adjust to different screen sizes and devices. This adaptability ensures that content remains accessible and readable on any platform.
3. Cross-Platform Development Tools:
Tools like React Native and Flutter enable developers to create applications that work seamlessly on both iOS and Android platforms. These cross-platform development tools reduce the need for duplicate coding efforts and ensure consistent accessibility features across different devices.
4. Accessibility Testing Tools:
Comprehensive accessibility testing tools, such as Axe, Lighthouse, and Wave, help developers identify and fix accessibility issues across various platforms. These tools provide detailed reports and recommendations for improving compliance with website accessibility standards like WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
5. Interoperability Standards:
Interoperability standards, such as the Accessible Rich Internet Applications (ARIA) specification, enhance the accessibility of web content by defining ways to make web applications more compatible with assistive technologies. By adhering to these standards, developers can ensure that their digital content is accessible to users relying on various assistive devices and software.
In conclusion, technological innovations in AI, assistive technologies, and cross-platform solutions are significantly advancing digital accessibility. By leveraging these tools and frameworks, businesses and developers can create more inclusive digital environments that cater to the diverse needs of all users.
Best Practices for Businesses in 2024
Integrating Accessibility from the Start
Incorporating accessibility from the initial stages of design and development is crucial for creating inclusive digital experiences. This approach ensures that accessibility is not an afterthought but an integral part of the development process. Key strategies and frameworks for integrating accessibility include:
1. Adopting Inclusive Design Principles:
Inclusive design principles prioritize the needs of all users, including those with disabilities, from the very beginning. By considering a diverse range of abilities and perspectives during the design phase, businesses can create products that are usable by a broader audience.
2. Utilizing Accessibility Guidelines:
Following established accessibility guidelines, such as the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), provides a solid foundation for building accessible digital platforms. These guidelines offer specific criteria for making web content more accessible to people with disabilities.
3. Incorporating Accessibility Features in Design Mockups:
During the design phase, include accessibility features such as keyboard navigation, screen reader compatibility, and color contrast adjustments in mockups and prototypes. This practice ensures that these elements are considered and refined before development begins.
4. Involving Accessibility Experts:
Engage accessibility experts early in the project to provide guidance and insights on best practices. Their expertise can help identify potential issues and suggest solutions that might not be apparent to those without specialized knowledge.
Continuous Testing and User Feedback
Regular accessibility testing and user feedback are essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring that digital platforms remain accessible over time. Key tools and methodologies for ongoing accessibility evaluation include:
1. Automated Accessibility Testing Tools:
Utilize automated testing tools like Axe, Lighthouse, and WAVE to regularly scan digital platforms for accessibility issues. These tools can quickly identify common problems and provide recommendations for remediation.
2. Manual Testing:
Conduct manual testing to evaluate aspects of accessibility that automated tools may miss, such as keyboard navigation and screen reader usability. Involve users with disabilities in testing to gain firsthand insights into their experiences and challenges.
3. User Feedback Mechanisms:
Implement mechanisms for collecting user feedback on accessibility. This can include surveys, feedback forms, and direct user testing sessions. Use this feedback to identify areas for improvement and make iterative enhancements.
4. Accessibility Audits:
Perform regular accessibility audits to assess the overall compliance of digital platforms with accessibility standards. Audits can be conducted by internal teams or external consultants to provide an objective evaluation.
Training and Awareness
Educating teams about accessibility best practices is vital for fostering a culture of inclusivity within an organization. Resources for staying updated on accessibility trends and standards include:
1. Accessibility Training Programs:
Offer comprehensive training programs for designers, developers, content creators, and project managers on accessibility principles and techniques. Training can cover topics such as WCAG compliance, assistive technology, and inclusive design.
2. Workshops and Webinars:
Host workshops and webinars with accessibility experts to provide ongoing education and keep teams informed about the latest trends and best practices. These sessions can also serve as forums for discussing challenges and sharing solutions.
3. Accessibility Resources and Documentation:
Maintain a repository of accessibility resources, including guidelines, checklists, and tutorials, that team members can reference during their work. Ensure that these resources are easily accessible and regularly updated.
4. Stay Informed About Web Accessibility Standards:
Encourage teams to stay updated on changes to website accessibility standards and regulations. Subscribe to newsletters, follow relevant blogs, and participate in industry conferences to keep abreast of the latest developments.
5. Promote an Inclusive Culture:
Foster an organizational culture that values accessibility and inclusivity. Highlight the importance of accessibility in company communications and recognize team members who contribute to accessibility initiatives.
By integrating accessibility from the start, conducting continuous testing, and prioritizing training and awareness, businesses can create digital platforms that are not only compliant with standards but also truly inclusive for all users.
Case Studies and Examples
Success Stories
Highlighting companies and projects that have excelled in digital accessibility can provide valuable insights and inspiration for others. Here are a few notable examples:
1. Microsoft’s Accessibility Initiatives:
- Overview: Microsoft has been a leader in promoting digital accessibility, integrating accessibility features across its products and services.
- Innovative Solutions: The company’s Xbox Adaptive Controller is a standout example, designed specifically for gamers with limited mobility. Microsoft also developed the Seeing AI app, which uses AI to describe the world to visually impaired users through their smartphones.
- Impact: These initiatives have significantly enhanced the inclusivity of Microsoft’s products, making them accessible to a broader audience.
2. Apple’s Commitment to Accessibility:
- Overview: Apple is renowned for its comprehensive approach to accessibility, embedding features directly into its operating systems.
- Innovative Solutions: VoiceOver, a screen reader integrated into all Apple devices, allows visually impaired users to navigate their devices using gestures and spoken feedback. Additionally, features like Switch Control provide alternative input methods for users with motor disabilities.
- Impact: Apple’s commitment to accessibility has set a high standard in the industry, demonstrating how inclusivity can be seamlessly integrated into mainstream products.
3. Bank of America’s Accessible Banking:
- Overview: Bank of America has made significant strides in ensuring its digital banking services are accessible to all customers.
- Innovative Solutions: The bank’s mobile app includes features like voice navigation, large text options, and compatibility with screen readers. They also provide accessible ATMs with audio assistance for visually impaired users.
- Impact: These efforts have made financial services more accessible, allowing customers with disabilities to manage their finances independently.
4. BBC’s Accessible Content Initiatives:
- Overview: The BBC has been proactive in making its digital content accessible to all viewers and users.
- Innovative Solutions: The BBC provides subtitles and audio descriptions for a significant portion of its broadcast content. Additionally, their website adheres to stringent website accessibility standards, ensuring that articles, videos, and interactive content are accessible.
- Impact: By prioritizing accessibility, the BBC has ensured that its diverse audience can access its wide range of content without barriers.
Learning from Challenges
While there are many success stories, there are also instances where a lack of accessibility has caused significant issues. Learning from these challenges is crucial to avoid similar pitfalls.
1. Target’s Website Accessibility Lawsuit:
- Challenge: In 2006, Target faced a lawsuit alleging that its website was not accessible to visually impaired users, violating the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA).
- Impact: The lawsuit resulted in a settlement, with Target agreeing to make its website accessible and pay damages. The case highlighted the legal and financial risks of neglecting digital accessibility.
- Lesson Learned: This incident underscores the importance of ensuring compliance with web accessibility standards to avoid legal repercussions and enhance user inclusivity.
2. Netflix’s Accessibility Complaints:
- Challenge: Netflix faced criticism and legal action for not providing captions for all its streaming content, making it inaccessible to users with hearing impairments.
- Impact: Following the lawsuit, Netflix agreed to caption all its streaming content and improve its accessibility features.
- Lesson Learned: This case emphasizes the need to provide accessible media content, including captions and audio descriptions, to meet the needs of users with disabilities and comply with accessibility regulations.
3. University Websites and Accessibility:
- Challenge: Several universities have faced legal action due to inaccessible websites, which hindered students with disabilities from accessing important information and resources.
- Impact: These legal challenges led to settlements requiring the universities to overhaul their websites and implement comprehensive accessibility plans.
- Lesson Learned: Educational institutions must prioritize digital accessibility to ensure that all students have equal access to information and resources, thereby avoiding legal issues and promoting inclusivity.
4. Nike’s Website Accessibility Issues:
- Challenge: Nike faced a class-action lawsuit in 2017 for not making its website accessible to visually impaired users.
- Impact: The lawsuit prompted Nike to enhance its website’s accessibility features, such as improved screen reader compatibility and better keyboard navigation.
- Lesson Learned: This case highlights the importance of proactive accessibility measures in e-commerce to ensure that all customers can access and navigate online stores without barriers.
By examining these success stories and challenges, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of digital accessibility. Embracing best practices and learning from past mistakes can help organizations create more inclusive digital experiences for all users.
Final Thoughts
Digital accessibility is not just a regulatory requirement but a commitment to inclusivity and equal access for all users. As technology evolves, so too must our efforts to create accessible digital environments. Ensuring your digital platforms are accessible requires dedication, the right tools, and reliable partners.
One such partner is InfoStride, a leader in promoting digital accessibility. InfoStride is committed to helping businesses ensure their websites and digital products meet the highest web accessibility standards. With their expertise, you can navigate the complexities of accessibility compliance and create inclusive experiences for all users.
InfoAccess: Your Free Website Accessibility Checker
To support businesses in their accessibility journey, InfoStride, a leading web application development services provider, offers InfoAccess, a powerful and free website accessibility checker. InfoAccess scans your website against all levels of the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), providing comprehensive insights into your website’s accessibility status. This tool identifies potential issues and offers actionable recommendations to help you achieve full compliance and improve user experience.
With InfoAccess, you can easily:
- Scan for WCAG Compliance: Check your website against WCAG 2.0 and WCAG 2.1 guidelines, ensuring you meet all necessary website accessibility standards.
- Identify Accessibility Issues: Discover barriers that might prevent users with disabilities from fully engaging with your website.
- Receive Actionable Insights: Get clear, actionable recommendations to fix identified issues and enhance your website’s accessibility.
Take the first step towards creating a more inclusive digital presence. Check your website’s accessibility now with InfoAccess and ensure you are meeting the needs of all users.
By prioritizing accessibility, you not only comply with legal requirements but also demonstrate your commitment to inclusivity, opening your digital doors to a broader audience. Partner with InfoStride and leverage InfoAccess to lead the way in digital accessibility.