Procurement in educational institutions is a complex but crucial function that ensures the seamless acquisition of goods and services necessary for daily operations and long-term goals. Whether it’s acquiring classroom materials, technological resources, or facilities management services, an effective procurement process is foundational to the success of schools, colleges, and universities.
Defining the Procurement Process in Educational Institutions
Procurement Meaning: In the realm of education, procurement encompasses all activities related to acquiring the goods and services required for institutional operations. This process is not merely about purchasing but involves a comprehensive approach to identifying needs, evaluating options, negotiating terms, and managing contracts to ensure optimal value and compliance with regulations.
Procurement Process: The procurement process in educational settings is a systematic approach that typically includes several key steps. Each step is designed to ensure that resources are obtained efficiently and economically, aligning with the institution’s objectives and regulatory requirements.
Common Procurement Process Steps in Schools, Colleges, and Universities
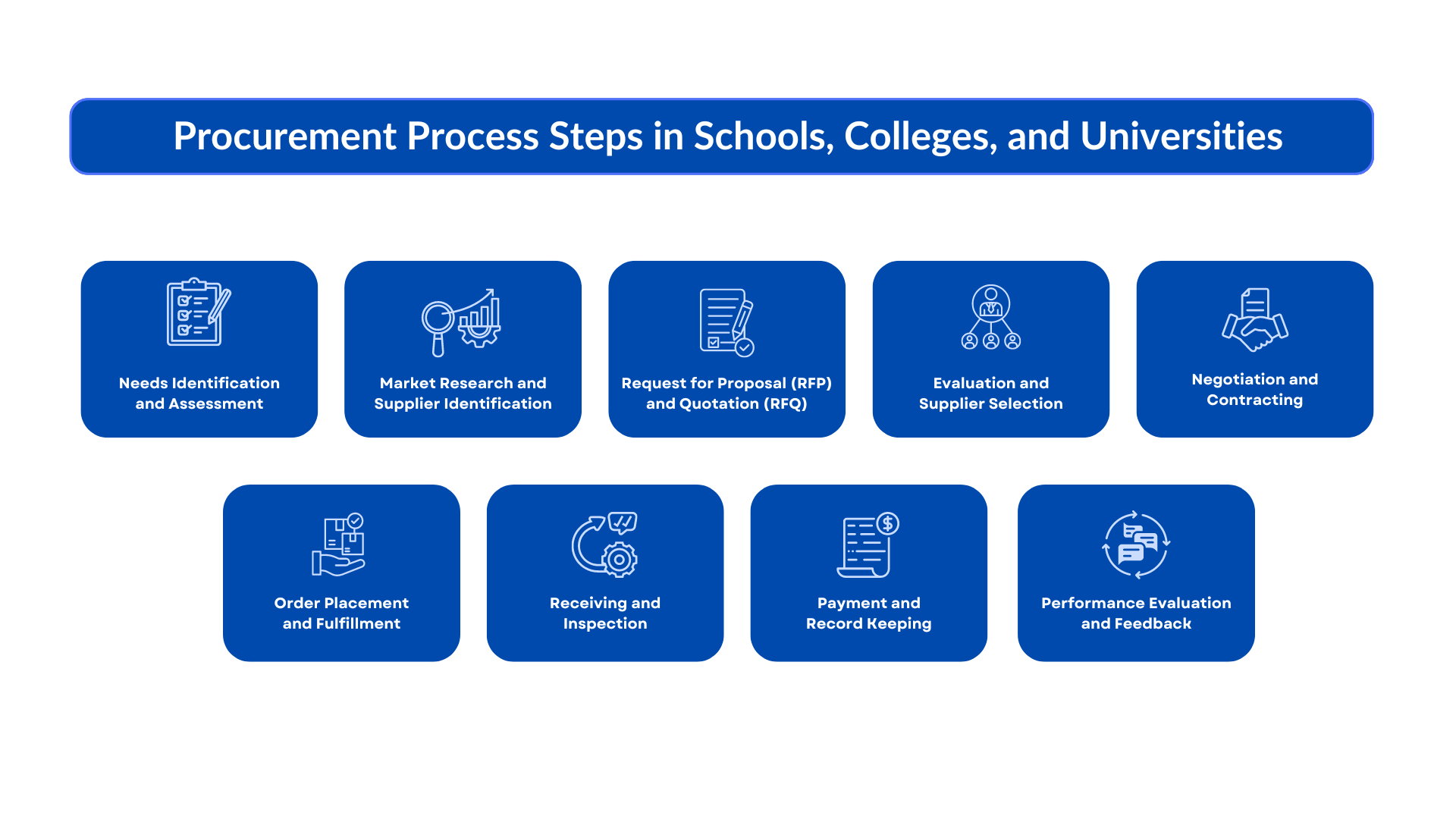
1. Needs Identification and Assessment:
- The first step involves identifying the specific goods and services required by the institution. This can range from everyday classroom supplies to specialized equipment or outsourced services.
- Needs assessment often includes input from various stakeholders, including faculty, staff, and administrative departments, to ensure that all requirements are accurately captured.
2. Market Research and Supplier Identification:
- Once needs are identified, the next step is to research the market to find potential suppliers or service providers who can meet these requirements.
- This involves evaluating suppliers based on criteria such as price, quality, reliability, and compliance with educational standards and regulations.
3. Request for Proposal (RFP) and Quotation (RFQ):
- Educational institutions typically issue RFPs or RFQs to solicit detailed proposals or quotations from suppliers. These documents outline the institution’s requirements and invite suppliers to submit their bids.
- This step is crucial for ensuring transparency and competitive pricing.
4. Evaluation and Supplier Selection:
- After receiving proposals or quotes, the institution evaluates each bid against predefined criteria to select the most suitable supplier.
- Factors considered include cost, quality, delivery timelines, and the supplier’s track record.
5. Negotiation and Contracting:
- Once a supplier is chosen, negotiations are conducted to finalize the terms of the purchase, including pricing, delivery schedules, and payment terms.
- A formal contract is then established, outlining all agreed-upon terms and conditions to protect both parties’ interests.
6. Order Placement and Fulfillment:
- With a contract in place, the institution places an official order with the supplier.
- The supplier then fulfills the order as per the agreed terms, delivering the goods or services within the specified timeframe.
7. Receiving and Inspection:
- Upon delivery, the institution inspects the goods or services to ensure they meet the required standards and specifications.
- Any discrepancies or issues are addressed promptly with the supplier.
8. Payment and Record Keeping:
- After successful receipt and inspection, the institution processes the payment as per the contract terms.
- Detailed records of the procurement transaction are maintained for auditing and future reference.
9. Performance Evaluation and Feedback:
- Post-purchase, the performance of both the supplier and the procured goods or services is evaluated.
- Feedback is used to inform future procurement decisions and improve supplier relationships.
Challenges Specific to Procurement in Education
Procurement in the education sector presents unique challenges that require careful management:
1. Budget Constraints:
- Educational institutions often operate under tight budgetary constraints, necessitating a careful balance between cost and quality.
- Managing limited financial resources while meeting the diverse needs of the institution can be challenging, particularly in public and non-profit educational settings.
2. Regulatory Compliance:
- Procurement processes in education must adhere to strict regulatory frameworks and compliance standards.
- This includes adhering to public procurement laws, ethical sourcing guidelines, and institutional policies, all of which add layers of complexity to the process.
3. Stakeholder Involvement:
- Procurement decisions in educational institutions involve input from multiple stakeholders, including academic and administrative staff, each with their own priorities and requirements.
- Balancing these diverse needs while ensuring a smooth procurement process can be complex and time-consuming.
4. Supplier Diversity and Quality:
- Ensuring a diverse supplier base that can consistently provide high-quality goods and services is a critical challenge.
- Educational institutions must evaluate and manage their suppliers effectively to avoid disruptions and maintain high standards.
5. Technological Integration:
- Integrating modern procurement tools and technologies can streamline processes but also requires investment and training.
- Many educational institutions face challenges in adopting and optimizing new procurement management systems due to resource constraints or resistance to change.
Understanding these challenges and the procurement process steps is essential for educational institutions aiming to streamline their procurement activities. By addressing these areas effectively, institutions can enhance their operational efficiency, reduce costs, and better support their educational missions.
Key Elements of Procurement Management in Education
Procurement management is the backbone of efficient and effective operations in educational institutions. It encompasses a range of activities designed to ensure that the procurement process—from identifying needs to acquiring goods and services—is conducted in a manner that supports the institution’s educational and operational goals.
What is Procurement Management?
Procurement Management refers to the comprehensive process of planning, organizing, and overseeing the acquisition of goods and services. In the context of educational institutions, procurement management involves:
- Strategic Planning: Aligning procurement activities with the institution’s strategic objectives to ensure resources are available to support teaching, research, and operational needs.
- Supplier Management: Building and maintaining relationships with suppliers to secure high-quality products and services at competitive prices.
- Contract Negotiation: Crafting and negotiating contracts that clearly define the terms of procurement to protect the interests of the institution.
- Risk Management: Identifying potential risks in the procurement process and implementing strategies to mitigate these risks, such as ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and ethical sourcing practices.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously assessing the effectiveness of procurement activities and supplier performance to identify areas for improvement.
In educational institutions, efficient procurement management is crucial for several reasons:
- Cost Efficiency: Educational budgets are often limited, making it essential to obtain goods and services at the best possible value. Effective procurement management helps institutions maximize their purchasing power and achieve cost savings.
- Resource Allocation: Proper procurement management ensures that resources are available when needed, avoiding disruptions in the academic and operational activities of the institution.
- Quality Assurance: By carefully managing suppliers and contracts, institutions can ensure they receive high-quality products and services that meet their specific needs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Educational institutions must adhere to strict procurement regulations and ethical standards. Effective procurement management ensures compliance with these requirements, reducing the risk of legal and financial penalties.
- Strategic Advantage: Well-managed procurement processes can give institutions a strategic advantage by supporting innovation and responsiveness to changing educational needs.
Also Read: IT Staff Augmentation Trends in 2024
Procurement Management System Features for the Education Sector
A Procurement Management System (PMS) is a digital platform that automates and streamlines procurement activities. For educational institutions, a robust PMS offers features tailored to their unique needs, including:
1. Centralized Procurement Portal:
- A centralized platform where all procurement activities can be managed and monitored.
- Facilitates collaboration among departments and stakeholders, ensuring transparency and consistency in procurement processes.
2. Automated Requisition and Approval Workflows:
- Automation of requisition and approval processes helps speed up procurement activities and reduces the administrative burden.
- Customizable workflows ensure that requests are reviewed and approved by the appropriate personnel, maintaining control and oversight.
3. Supplier Management and Evaluation Tools:
- Tools for managing supplier information, performance evaluations, and contract details.
- Enables institutions to maintain a database of preferred suppliers and track their performance over time, ensuring reliable and quality partnerships.
4. Budget Management and Cost Control:
- Features that integrate with the institution’s financial systems to monitor budgets and track expenditures in real-time.
- Helps prevent overspending and ensures procurement activities are aligned with budgetary constraints.
5. Compliance and Risk Management:
- Built-in compliance features that ensure procurement activities adhere to regulatory requirements and institutional policies.
- Risk management tools to identify and mitigate potential procurement risks, such as supplier reliability and ethical sourcing issues.
6. Analytics and Reporting:
- Advanced analytics and reporting capabilities provide insights into procurement performance and spending patterns.
- Data-driven insights help institutions identify areas for improvement and make informed strategic decisions.
7. Catalog Management and E-Procurement:
- Digital catalogs that allow staff to browse and order from a pre-approved list of suppliers and products.
- E-procurement capabilities streamline the ordering process and ensure that purchases are made from trusted sources.
8. Integration with Educational Systems:
- Seamless integration with other institutional systems, such as financial management and inventory systems.
- Ensures data consistency and allows for efficient cross-functional collaboration.
Procurement Management in Education: Efficient procurement management in educational institutions is not just about acquiring goods and services. It is about strategically managing procurement activities to support the institution’s mission, enhance operational efficiency, and ensure compliance with regulatory and budgetary requirements. A well-designed procurement management system plays a pivotal role in achieving these objectives by providing the tools and capabilities needed to streamline and optimize procurement processes.
Steps to Streamline the Procurement Process in Education
Streamlining the procurement process in educational institutions is essential for enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring timely access to the resources needed for effective teaching and learning. By adopting a structured approach to evaluate and optimize procurement activities, schools, colleges, and universities can significantly improve their operational effectiveness. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help educational institutions streamline their procurement processes:
1. Assess Current Procurement Processes
Evaluate Existing Procedures:
- Begin by conducting a thorough assessment of your current procurement process. Document each step from needs identification to supplier payment and delivery management.
- Engage with stakeholders across departments, including faculty, administration, and finance, to gather insights into their procurement experiences and challenges.
Analyze Process Effectiveness:
- Review procurement data and metrics to understand the performance of your current processes. Look at metrics such as procurement cycle time, cost savings, supplier performance, and compliance rates.
- Identify areas where the process is working well and areas that require improvement.
Benchmark Against Best Practices:
- Compare your institution’s procurement processes with industry best practices and standards. This can help identify gaps and areas for enhancement.
- Consider consulting with procurement experts or peers in the education sector to gain insights into effective procurement strategies and practices.
2. Identify Bottlenecks and Inefficiencies
Map Out Process Flows:
- Create detailed flowcharts of your procurement processes to visualize the steps involved and identify potential bottlenecks or delays.
- Pay attention to repetitive tasks, approval bottlenecks, and any points where the process stalls or requires manual intervention.
Gather Stakeholder Feedback:
- Conduct surveys or hold focus group discussions with staff involved in procurement to identify common pain points and sources of frustration.
- Listen to feedback from suppliers and vendors to understand their perspective on how the procurement process can be improved.
Analyze Root Causes:
- Use techniques such as root cause analysis to delve into the underlying reasons for inefficiencies. For example, if purchase approvals are consistently delayed, investigate whether it’s due to unclear policies, lack of accountability, or excessive manual steps.
- Prioritize the issues based on their impact on the overall procurement process and the institution’s operations.
3. Leverage Technology and Procurement Tools
Implement a Procurement Management System (PMS):
- Invest in a robust procurement management system that automates and integrates all aspects of the procurement process. A PMS can centralize procurement activities, streamline communication, and provide real-time visibility into procurement operations.
- Ensure that the system includes features such as e-procurement, supplier management, budget tracking, and compliance monitoring to address the specific needs of educational institutions.
Utilize E-Procurement Solutions:
- Adopt e-procurement platforms that allow staff to browse and order from approved suppliers online. This can simplify the purchasing process, reduce paperwork, and ensure compliance with procurement policies.
- E-procurement tools also provide access to a wider range of suppliers and products, enabling institutions to compare prices and select the best options.
Integrate with Existing Systems:
- Ensure that your procurement tools are integrated with other institutional systems, such as financial management, inventory control, and ERP systems. This integration helps maintain data consistency and supports seamless workflow automation.
- Integration can also facilitate better financial planning and budget management by providing comprehensive visibility into procurement expenditures.
Leverage Data and Analytics:
- Use data analytics tools to gain insights into procurement performance, supplier metrics, and spending patterns. Advanced analytics can help identify trends, forecast needs, and uncover opportunities for cost savings.
- Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and regularly review them to monitor the effectiveness of your procurement strategies and make data-driven decisions.
4. Standardize and Automate Procurement Workflows
Develop Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs):
- Create clear, standardized procedures for each step of the procurement process. SOPs should outline the roles and responsibilities of all stakeholders, approval workflows, and compliance requirements.
- Make these procedures easily accessible to all staff involved in procurement to ensure consistency and adherence to best practices.
Automate Routine Tasks:
- Automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks such as purchase requisition approvals, order processing, and invoice matching. Automation reduces manual effort, speeds up the procurement cycle, and minimizes the risk of errors.
- Consider using workflow automation tools that can be customized to match your institution’s specific procurement policies and procedures.
Implement Self-Service Procurement:
- Enable staff to initiate and manage their procurement needs through self-service portals. This can empower departments to handle their purchasing requirements while adhering to institutional guidelines and controls.
- Self-service procurement reduces the burden on procurement teams and speeds up the procurement process for routine purchases.
Monitor and Optimize Continuously:
- Establish a continuous improvement cycle by regularly reviewing procurement performance and seeking feedback from users.
- Stay updated with the latest procurement technologies and practices to keep your processes aligned with evolving educational needs and industry trends.
By following these steps, educational institutions can streamline their procurement processes, leading to increased efficiency, cost savings, and better alignment with their educational goals. Streamlining the procurement process not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances the institution’s ability to respond quickly to changing needs and opportunities.
Case Study/Examples of Streamlined Procurement in Education
Streamlining procurement processes can significantly enhance the operational efficiency and financial management of educational institutions. Below are real-life examples and case studies of how various schools, colleges, and universities have successfully optimized their procurement activities using innovative tools and strategies.
1. University of California, Berkeley – Implementing a Comprehensive Procurement Management System
Overview: The University of California, Berkeley, a leading public research university, faced challenges with fragmented and manual procurement processes that led to inefficiencies and high operational costs. To address these issues, the university implemented a comprehensive Procurement Management System (PMS).
Tools and Strategies:
- Centralized Procurement Platform: UC Berkeley adopted a centralized e-procurement platform called BearBuy, which integrates all procurement activities across the campus.
- Automated Workflows: The system automated procurement workflows, including requisition approvals and order processing, reducing the need for manual intervention and speeding up the procurement cycle.
- Supplier Management: BearBuy provided robust supplier management features, allowing the university to maintain a centralized supplier database and streamline vendor evaluation and selection.
- User Training and Adoption: The university invested in training programs to ensure that faculty and staff were proficient in using the new system, leading to high adoption rates and minimal disruptions during the transition.
Outcomes:
- Increased Efficiency: The centralized and automated processes significantly reduced the time required for procurement activities, improving overall operational efficiency.
- Cost Savings: Enhanced supplier negotiations and consolidated purchasing led to substantial cost savings.
- Compliance and Transparency: The new system ensured compliance with procurement policies and provided greater transparency into spending and supplier performance.
2. Harvard University – Leveraging E-Procurement Solutions for Academic Resources
Overview: Harvard University, one of the world’s most prestigious institutions, sought to improve the efficiency of its procurement process for academic resources and reduce the administrative burden on its departments. Harvard adopted an e-procurement solution specifically designed for educational institutions.
Tools and Strategies:
- E-Procurement Platform: Harvard implemented an e-procurement platform that allowed faculty and staff to order academic resources, such as books, lab supplies, and software, from pre-approved suppliers through a user-friendly online catalog.
- Digital Approval Processes: The platform automated the approval processes for purchase requests, ensuring that orders were quickly reviewed and approved without unnecessary delays.
- Supplier Partnerships: Harvard established strategic partnerships with key suppliers, negotiating better pricing and service terms for frequently ordered items.
- Analytics and Reporting: The e-procurement system provided detailed analytics and reporting capabilities, giving the university insights into spending patterns and opportunities for further cost reductions.
Outcomes:
- Streamlined Ordering: Faculty and staff could easily order and track academic resources, reducing the administrative load and enabling them to focus more on their core educational responsibilities.
- Improved Spend Management: The platform’s analytics capabilities helped the university identify areas where it could optimize spending and achieve additional cost savings.
- Enhanced Supplier Relationships: Strategic supplier partnerships led to improved service levels and better value for money.
3. University of New South Wales (UNSW), Australia – Standardizing and Automating Procurement Workflows
Overview: The University of New South Wales (UNSW) in Australia faced challenges with inconsistent and manual procurement processes across its diverse departments. To address these issues, UNSW standardized and automated its procurement workflows using a specialized procurement management system.
Tools and Strategies:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): UNSW developed and implemented standardized operating procedures for all procurement activities, ensuring consistency and compliance across the institution.
- Procurement Management System: The university adopted a procurement management system that integrated with its existing financial systems, providing a seamless workflow from requisition to payment.
- Automation of Routine Tasks: Routine procurement tasks, such as purchase order generation and invoice matching, were automated, reducing the time and effort required for these activities.
- Self-Service Procurement: The system enabled departments to manage their procurement needs through a self-service portal, streamlining the ordering process and reducing dependency on the central procurement office.
Outcomes:
- Operational Consistency: The standardized procedures and automated workflows ensured that procurement processes were consistent and compliant across all departments.
- Time Savings: Automation of routine tasks and self-service capabilities significantly reduced the administrative burden on the procurement team and other staff members.
- Enhanced Visibility: The integration of the procurement system with financial systems provided real-time visibility into procurement activities and expenditures, aiding in better financial management.
4. K-12 School Districts in the US – Collaborative Procurement Strategies
Overview: Several K-12 school districts in the United States have adopted collaborative procurement strategies to enhance their purchasing power and reduce costs. By pooling resources and leveraging collective buying power, these districts have successfully streamlined their procurement processes.
Tools and Strategies:
- Consortium Purchasing: School districts formed purchasing consortia to negotiate bulk purchasing agreements with suppliers, obtaining discounts and favorable terms that individual schools could not achieve alone.
- Shared Procurement Platforms: The consortia used shared procurement platforms that allowed member schools to access pre-negotiated contracts and streamline the ordering process.
- Centralized Contract Management: Centralized management of contracts and supplier relationships ensured consistency and efficiency across the districts.
- Training and Support: The consortia provided training and support to member schools to facilitate the adoption of new procurement practices and tools.
Outcomes:
- Cost Reduction: Collaborative purchasing agreements resulted in significant cost savings on commonly purchased items and services.
- Improved Supplier Access: Schools gained access to a wider range of high-quality suppliers and products through the consortia.
- Streamlined Processes: Shared platforms and centralized management simplified procurement processes, reducing administrative overhead and improving efficiency.
These case studies illustrate how educational institutions can effectively streamline their procurement processes through strategic planning, technology adoption, and collaboration. By leveraging procurement tools and adopting best practices, schools, colleges, and universities can achieve greater efficiency, cost savings, and enhanced operational effectiveness.
Role of Technology in Streamlining Procurement in Education
In the rapidly evolving landscape of education, technology plays a crucial role in transforming and streamlining procurement processes. Educational institutions, ranging from K-12 schools to large universities, are increasingly turning to digital tools and procurement management systems to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve the overall procurement experience. This section delves into how these technologies are facilitating better procurement practices and explores the latest advancements in procurement technology relevant to the education sector.
The Power of Digital Tools in Procurement Management
Digital tools have revolutionized procurement management by automating and simplifying various aspects of the procurement process. Here’s how these tools contribute to streamlining procurement in educational institutions:
1. Centralized Procurement Management Systems (PMS):
- Integration and Automation: A Procurement Management System (PMS) integrates all procurement activities into a single platform, automating workflows from requisition to payment. This centralization reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and speeds up the procurement cycle.
- Real-time Visibility: PMS provides real-time visibility into procurement processes and expenditures. This transparency enables educational institutions to monitor procurement activities, track spending, and ensure compliance with budgetary constraints and policies.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Advanced PMS features include analytics and reporting capabilities that offer insights into procurement performance and trends. Educational institutions can use these insights to make informed, strategic decisions about their procurement practices.
2. E-Procurement Platforms:
- Streamlined Ordering: E-procurement platforms allow users to browse digital catalogs, place orders, and manage procurement requests online. These platforms simplify the ordering process, making it easy for staff to procure goods and services from pre-approved suppliers.
- Enhanced Supplier Management: E-procurement systems often include tools for managing supplier information and relationships. Educational institutions can maintain a database of preferred suppliers, track performance, and negotiate better terms.
- Compliance and Control: E-procurement tools enforce compliance with institutional procurement policies and procedures. Automated approval workflows and audit trails ensure that all purchases are reviewed and authorized according to established guidelines.
3. Mobile and Cloud-Based Solutions:
- Anywhere, Anytime Access: Cloud-based procurement solutions provide flexibility by allowing users to access the system from anywhere with an internet connection. Mobile apps further enhance accessibility, enabling procurement activities on the go.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud solutions are scalable, making them suitable for educational institutions of all sizes. They can easily accommodate changing needs and growing procurement volumes without requiring significant infrastructure investments.
4. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML):
- Predictive Analytics: AI and ML algorithms can analyze historical procurement data to predict future needs and identify trends. This capability helps educational institutions anticipate demand, optimize inventory, and make proactive purchasing decisions.
- Process Automation: AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, such as invoice processing and supplier communication, freeing up staff to focus on more strategic activities.
- Enhanced Supplier Evaluation: AI can analyze supplier performance data to provide insights into reliability, quality, and risk factors, aiding in the selection and management of suppliers.
Advancements in Procurement Technology for Education
Recent advancements in procurement technology are transforming how educational institutions manage their procurement activities. Here are some cutting-edge technologies and their applications in the education sector:
1. Blockchain Technology:
- Transparent and Secure Transactions: Blockchain provides a decentralized and immutable ledger for recording transactions. This technology ensures transparency, security, and traceability in procurement activities, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing trust between institutions and suppliers.
- Smart Contracts: Blockchain enables the use of smart contracts—self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Smart contracts automate contractual obligations, such as payment release upon delivery of goods, ensuring timely and accurate execution of procurement agreements.
2. Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
- Task Automation: RPA uses software robots to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, such as data entry, order processing, and invoice reconciliation. This automation reduces manual workload, improves accuracy, and accelerates procurement processes.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: RPA can bridge gaps between modern procurement systems and legacy software, enabling seamless data flow and process continuity without the need for extensive system overhauls.
3. Internet of Things (IoT):
- Smart Inventory Management: IoT devices can monitor inventory levels in real-time, automatically triggering reorder requests when stock levels fall below predefined thresholds. This capability ensures that educational institutions maintain optimal inventory levels without manual intervention.
- Asset Tracking: IoT technology enables the tracking of assets and supplies within educational facilities, improving visibility and management of resources.
4. Advanced Analytics and Big Data:
- Spend Analysis: Advanced analytics tools can process large volumes of procurement data to identify spending patterns, cost-saving opportunities, and potential risks. Educational institutions can leverage these insights to optimize their procurement strategies and budgets.
- Supplier Risk Management: Big data analytics can evaluate supplier performance and risk factors, such as financial stability and compliance history, helping institutions make informed decisions about their supplier relationships.
Final Thoughts:
Streamlining procurement processes in the education sector is not just a matter of operational efficiency—it’s a vital component of ensuring that educational institutions can allocate their resources effectively and focus on their primary mission: delivering quality education. By adopting best practices, leveraging advanced procurement tools, and implementing innovative technologies, schools, colleges, and universities can overcome common procurement challenges, reduce costs, and improve the quality and timeliness of their acquisitions.
Efficient procurement processes lead to better management of educational resources, from everyday classroom supplies to advanced technological equipment. This streamlined approach not only supports the educational objectives but also enhances the institution’s ability to respond quickly to the evolving needs of students and staff.
Explore InfoStride’s E&I Staffing Services
For educational institutions looking to enhance their procurement efficiency, InfoStride offers specialized services through the E&I Cooperative Services. Our partnership with E&I is designed to support the unique needs of the education community by providing both IT Staff Augmentation Services and Temporary Staffing solutions.
At InfoStride, we understand the importance of integrating qualified IT professionals into educational institutions to streamline operations and support various projects. With our extensive experience and a strong foundation as a certified M/WBE Business Enterprise Firm, we are well-equipped to deliver tailored staffing services that meet the specific requirements of educational entities.
What InfoStride Offers:
- IT Staff Augmentation: We provide access to a curated database of highly skilled IT professionals, including roles in engineering, administration, development, quality assurance, and performance management. This ensures that your institution can quickly fill critical IT positions with qualified candidates.
- Temporary Staffing Services: Our services extend to temporary staffing, helping you meet short-term or project-based IT talent needs without the long-term commitment of full-time hires.
- Expertise in Education: Our team is experienced in serving both commercial and government entities, making us adept at navigating the unique challenges and requirements of the education sector.