In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are increasingly turning to outsourcing to accelerate software development while optimizing costs. According to a report by Deloitte, 70% of companies cite cost reduction as the primary reason for outsourcing software development. Among the most popular outsourcing models, offshore and nearshore development stand out, each offering distinct advantages depending on a company’s specific needs, budget, and operational priorities.
Choosing between offshore and nearshore development can be challenging, as both models come with unique benefits and trade-offs. This blog will break down the key differences between offshore and nearshore outsourcing, helping businesses determine the best approach for their software development needs. Additionally, we’ll explore how an Offshore Development Center(ODC)—like the one offered by InfoStride—can be a strategic choice for companies looking for scalability, efficiency, and top-tier talent.
Understanding Offshore and Nearshore Development
What is Offshore Development?
Offshore development refers to outsourcing software development to a team located in a distant country, often several time zones away. This model is widely adopted by businesses looking to leverage cost-efficient talent from global markets while maintaining flexibility in scaling their teams.
Popular offshore development regions include India, the Philippines, and Eastern Europe, where companies can access highly skilled developers at a fraction of the cost compared to hiring locally.
What is Nearshore Development?
Nearshore development involves outsourcing software development to a team located in a neighboring or nearby country, typically within the same or a similar time zone. This model provides a balance between cost savings and seamless collaboration, making it a preferred choice for companies that require frequent real-time communication.
Common nearshore outsourcing regions include Latin America for U.S.-based companies and Eastern Europe for Western European businesses.
Offshore vs. Nearshore: Key Differences
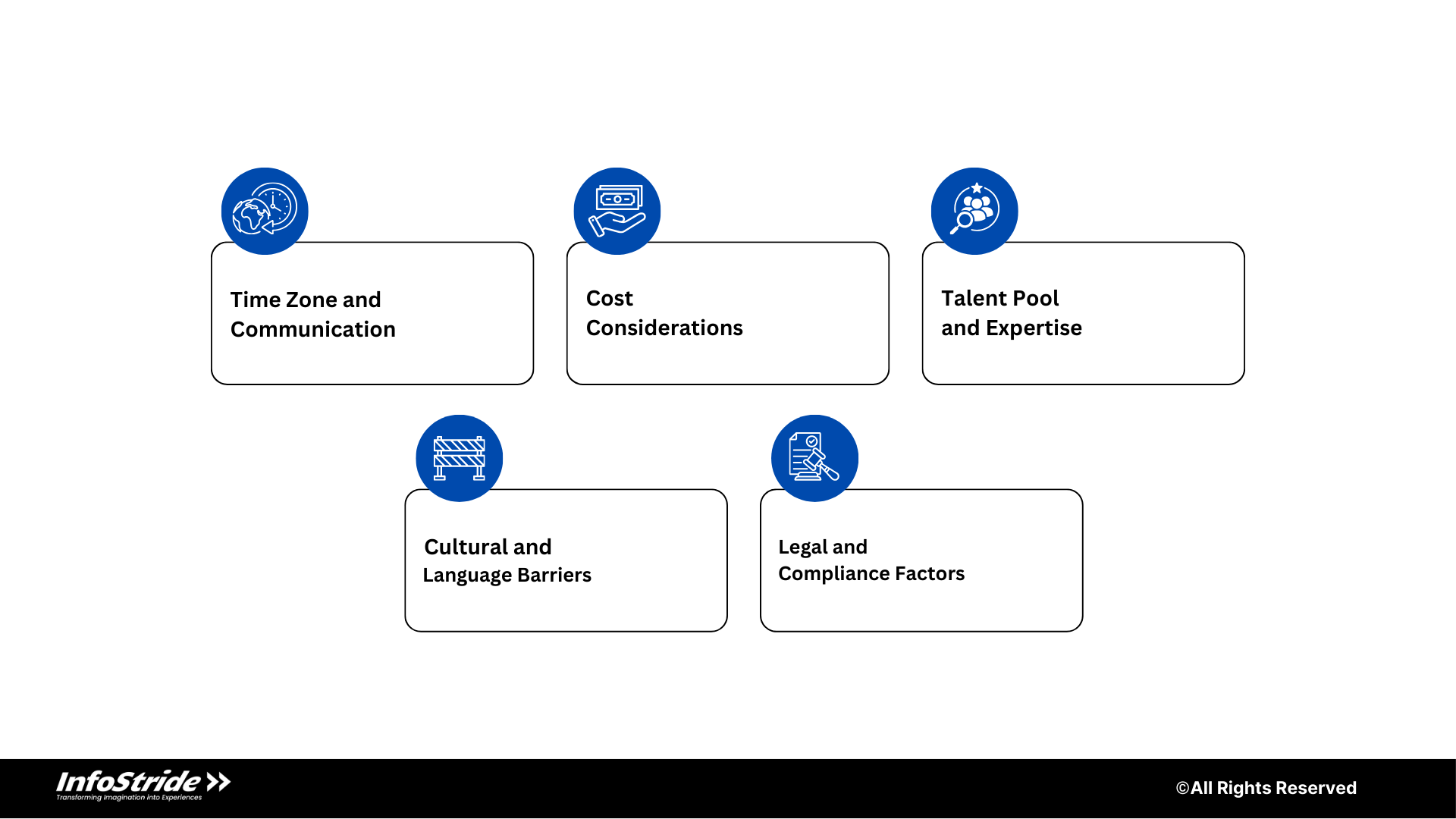
When deciding between offshore and nearshore development, businesses must consider several factors that impact project efficiency, collaboration, and cost-effectiveness. Below is a breakdown of the key differences between the two models.
Time Zone and Communication
- Offshore: Due to significant time zone differences, real-time communication can be challenging, potentially leading to delays in decision-making and project updates. However, offshore teams often implement asynchronous workflows and overlapping work hours to mitigate this issue.
- Nearshore: With similar or overlapping time zones, nearshore development enables smoother collaboration and faster response times, making it easier to schedule meetings, resolve issues, and maintain real-time communication.
Cost Considerations
- Offshore: Generally, offshore software development offers lower labor costs, making it the most cost-effective option for businesses looking to optimize their budgets. Countries like India and the Philippines provide top-tier software development services at significantly reduced rates compared to Western countries.
- Nearshore: While nearshore development is more affordable than onshore outsourcing, it typically comes at a higher cost than offshore due to factors like regional wage differences and economic conditions. However, businesses may justify the added expense for improved collaboration and efficiency.
Talent Pool and Expertise
- Offshore: Companies gain access to a vast and diverse talent pool, making it easier to find developers with specialized skills. Offshore locations often have well-established IT industries, producing a high volume of skilled software engineers.
- Nearshore: Nearshore teams consist of highly qualified professionals with strong regional expertise. While the talent pool may be smaller than offshore options, businesses benefit from closer alignment in industry standards and best practices.
Cultural and Language Barriers
- Offshore: There may be cultural and language barriers that can impact workflow and collaboration. Miscommunication and differing work cultures can sometimes slow down processes, though many offshore teams are trained to work with global clients.
- Nearshore: Since nearshore teams often share similar cultures and languages with their clients, collaboration is generally more seamless, reducing potential misunderstandings and ensuring smoother project execution.
Legal and Compliance Factors
- Offshore: Offshore outsourcing may involve navigating complex legal frameworks, data protection laws, and compliance challenges. Companies working in highly regulated industries (e.g., finance, healthcare) must ensure offshore teams meet security and compliance standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
- Nearshore: Since nearshore teams operate within similar legal and regulatory frameworks, businesses find it easier to manage compliance and mitigate risks. This is particularly beneficial for industries requiring strict adherence to data privacy and security regulations.
Real-World Use Cases: When to Choose Offshore vs. Nearshore
Choosing between offshore and nearshore development depends on a company’s unique needs, industry requirements, and long-term goals. Let’s look at how different types of businesses leverage these models to their advantage.
1. Startups & Small Businesses
Best fit: Offshore Development
Startups and small businesses often operate with limited budgets and tight timelines, making offshore development an ideal choice. By outsourcing to cost-effective regions like India or Eastern Europe, startups can access skilled developers at a fraction of local hiring costs while focusing their in-house resources on core business functions.
Example: Many early-stage SaaS startups outsource their MVP development to offshore teams to build their first product at a lower cost before raising funds for in-house expansion.
2. Enterprises & Large Corporations
Best fit: Nearshore Development (or Hybrid)
Enterprises dealing with complex software systems, frequent updates, and the need for real-time collaboration often choose nearshore outsourcing. The time zone alignment and cultural proximity help streamline workflows and communication.
Example: A U.S.-based Fortune 500 company outsourcing software maintenance and customer support to nearshore teams in Mexico or Argentina for easier coordination.
3. Regulated Industries (Healthcare, Finance, Government, etc.)
Best fit: Nearshore Development
Industries with strict data security, privacy, and regulatory compliance requirements (e.g., HIPAA for healthcare, GDPR for fintech) often prefer nearshore outsourcing. The proximity helps ensure adherence to regional laws and facilitates easier audits, security checks, and contract enforcement.
Example: A European fintech firm outsourcing software development to nearshore teams in Poland to ensure compliance with EU financial regulations.
4. Product-Based vs. Service-Based Companies
- Product-based companies (e.g., SaaS, eCommerce, Mobile Apps)
Best fit: Offshore for development, Nearshore for product management
Many product-based businesses leverage offshore teams for cost-effective feature development while keeping nearshore teams for customer-facing roles, UX/UI design, and product strategy.
Example: A U.S. eCommerce company outsourcing app development to offshore teams in Vietnam but keeping a nearshore product management team in Canada for seamless user experience optimization.
- Service-based companies (e.g., IT Consulting, Digital Agencies, BPOs)
Best fit: Hybrid Approach
Service-based businesses often juggle multiple clients with varied needs. A hybrid approach—where offshore teams handle backend development, testing, and support, while nearshore teams focus on client interactions and project management—works best.
Example: A digital agency in the UK working with offshore WordPress developers in India but keeping an onshore/nearshore client management team for better customer service.
The Hybrid Approach: Combining Offshore and Nearshore for Maximum Efficiency
While offshore and nearshore development each have their strengths, many companies combine both models to get the best of both worlds. A hybrid approach strategically blends cost savings, collaboration efficiency, and specialized expertise for maximum flexibility.
How Does the Hybrid Model Work?
Companies using a hybrid model distribute tasks between offshore and nearshore teams based on complexity, urgency, and collaboration needs. A common setup looks like this:
Offshore Teams (e.g., India, Philippines, Vietnam)
- Focus on cost-sensitive, scalable tasks
- Handle software development, QA testing, and infrastructure support
- Work in asynchronous environments with clear documentation
Nearshore Teams (e.g., Latin America, Eastern Europe, Canada)
- Manage client-facing roles, project coordination, and UX/UI design
- Oversee business-critical tasks that require real-time collaboration
- Serve as a bridge between offshore teams and in-house stakeholders
Benefits of the Hybrid Model
- Optimized Costs: Businesses save money by leveraging offshore teams for development while keeping nearshore teams for tasks requiring closer alignment.
- Enhanced Collaboration: The time zone proximity of nearshore teams ensures smooth communication, reducing project delays.
- Access to a Global Talent Pool: Companies can tap into specialized talent from different regions, ensuring they have the right expertise for each aspect of development.
- Scalability & Flexibility: A hybrid model allows businesses to scale development teams up or down based on project demands.
Real-World Example of the Hybrid Approach
A U.S.-based SaaS company looking to optimize its development process might:
- Offshore coding and software testing to a team in India to reduce costs.
- Nearshore UX/UI design and product management to a team in Mexico to ensure better communication and faster iterations.
- Keep a small in-house team to manage high-level strategy and client interactions.
By leveraging a hybrid approach, businesses balance efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and seamless project execution—making it a preferred model for companies scaling their software development operations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Choosing between offshore and nearshore development depends on factors like budget, collaboration needs, and project complexity. Offshore outsourcing provides cost savings and access to a diverse talent pool, while nearshore development ensures smoother communication and cultural alignment. A hybrid approach often strikes the right balance, allowing businesses to optimize costs while maintaining efficiency.
For companies seeking a dedicated, scalable solution, an Offshore Development Center (ODC) offers long-term benefits. InfoStride’s ODC services provide access to top-tier talent, seamless integration, and a tailored approach to meet your software development needs.